How is radio signal propagated. 2 Comparison of wired and wireless transmissions WiredWireless BandwidthDepending on the media used, can be large Narrow. - ppt download

3 Bandwidth Wired Twisted pair (twisted to reduce crosstalk effect) Telephones, DSL: Category 3 cabling, 16 MHz/10Mbps, mainly for voice, uses RJ-11 jack. Ethernet: Category 5 cabling, 4 pairs, 100Mbps, uses RJ- 45 jack. Coaxial cables (broadband coax): cable TV, cable modems, MHz bandwidth Optical fibers: wide bandwidth (10 GHz or higher), smaller size, lighter weight, long coverage, but expensive, less flexible. Power line Wireless
How is radio signal propagated
Ethernet: Category 5 cabling, 4 pairs, 100Mbps, uses RJ- 45 jack. Coaxial cables (broadband coax): cable TV, cable modems, MHz bandwidth Optical fibers: wide bandwidth (10 GHz or higher), smaller size, lighter weight, long coverage, but expensive, less flexible. Power line Wireless.
4 Frequency Bands of wireless Around 1 GHz, cellular, 25 to 30 MHz for forward or reverse link ( and MHz), 25/30 kHz per user (TDMA/FDD) 2 GHz, PCS (Personal Communications Service) and WLAN (Wireless Local Area Network) 5 GHz, WLAN IR frequencies for optical communications
Unlicensed bands are dedicated to certain usages. Anyone can use an unlicensed bands without a fee. The problem is interference. Example: microwave ovens and Wi-Fi devices..
6 Increase number of users FDMA, TDMA, CDMA Divide the coverage area into several cells and reuse the frequencies by restricting the signal strength of the transmitter in each cell SDMA: space division multiple access, uses directional antennas to divide a cell into several sections and interference can be reduced.
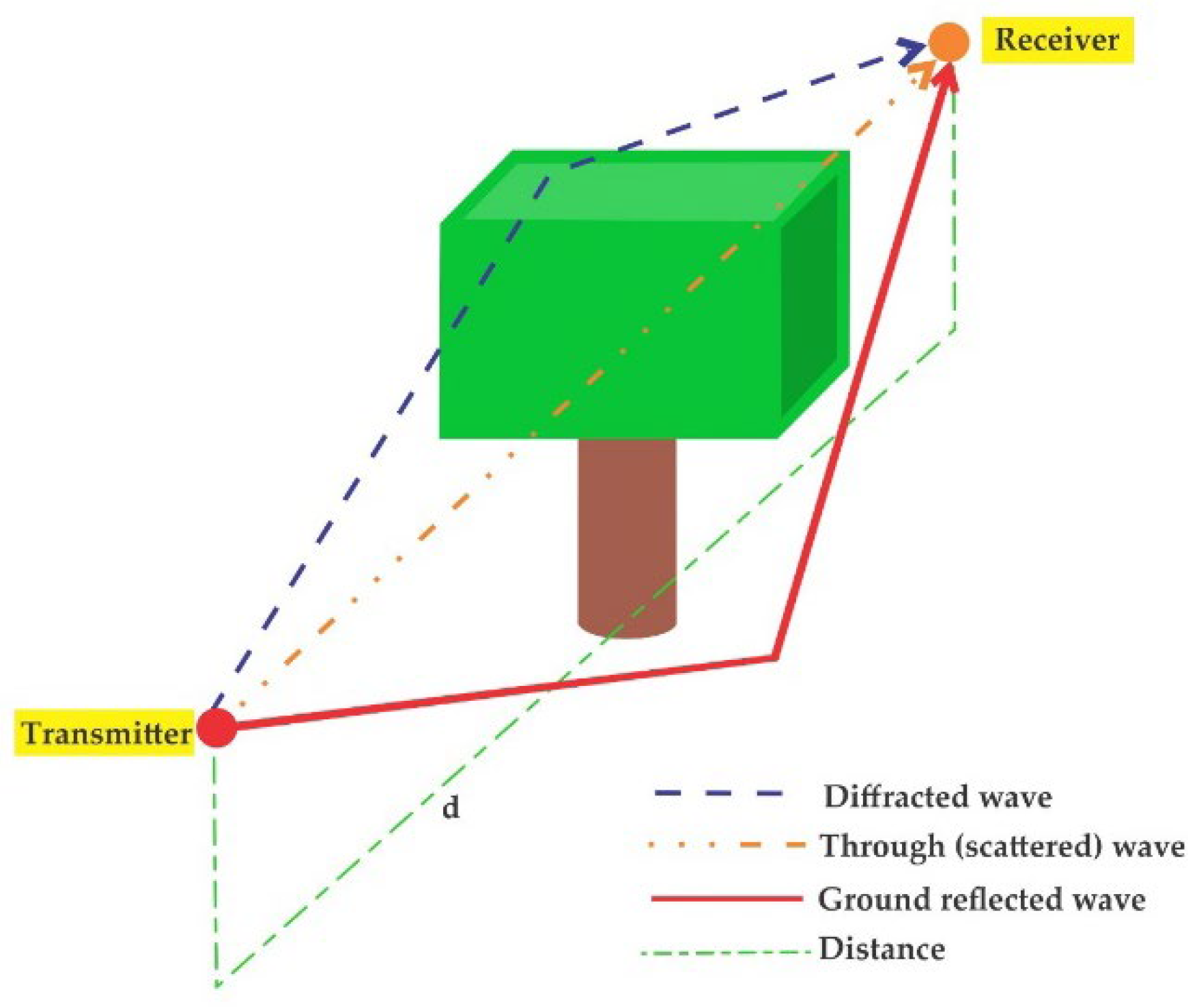
7 Radio propagation mechanisms Line-of-sight transmission Reflection Diffraction Scattering
8 Signal coverage Free space propagation
11 Compare path loss of wired and wireless Wireless: exponential Wired: linear Therefore for long distance transmission wired media is preferred (if laying cables is a viable option, of course).
It’s called slow fading because when distance changes the variations change much slower than other forms of fading do. It’s also called shadow fading because the variation is often due to the blocking of buildings, walls and other subjects. Additional signal strength is needed to cover the entire area..
Those signals (actually, they are copies of the same signal) come from the same source (transmitter), but travel through different paths. Some will reach the MS directly, some may be reflected by an object (e.g., a building) first and thus take longer paths. Those signals (copies of the same signal) arrive at a mobile station at different time instances—the one with a shorter path will arrive earlier than the one with a longer path. At the mobile station, those signals interfere with each other. Sometimes they can cancel each other out, but sometimes they can enhance each other. As a result, the received signal strength (the combination of those signals) varies rapidly as the mobile station moves. It’s called small- scale fading or fast fading..
Therefore a wide-band signal will be more robust against the frequency selective fading. For data transmission, error detection can detect and recover the lost data. Intersymbol Interference (ISI) caused by multipath is an important issue in wireless communications. 14.

WiFi Networking: Radio Wave Basics

04 transmission media
Sensors, Free Full-Text
Sensors, Free Full-Text

Chapter 2 Lecture.ppt - Chapter 2 Conducted and Radiated Media Introduction • The two major categories of media include: - Conducted wired media •

Data Communications and Networking: Wireless Communication and the Electromagnetic Spectrum
Cisco Networking, VPN Security, Routing, Catalyst-Nexus Switching, Virtualization Hyper-V, Network Monitoring, Windows Server, CallManager, Free Cisco Lab, Linux Tutorials, Protocol Analysis, CCNA, CCNP, CCIE. - Page #1

Wireless Propagation Effects And Their Impact On Reliable Transmissions
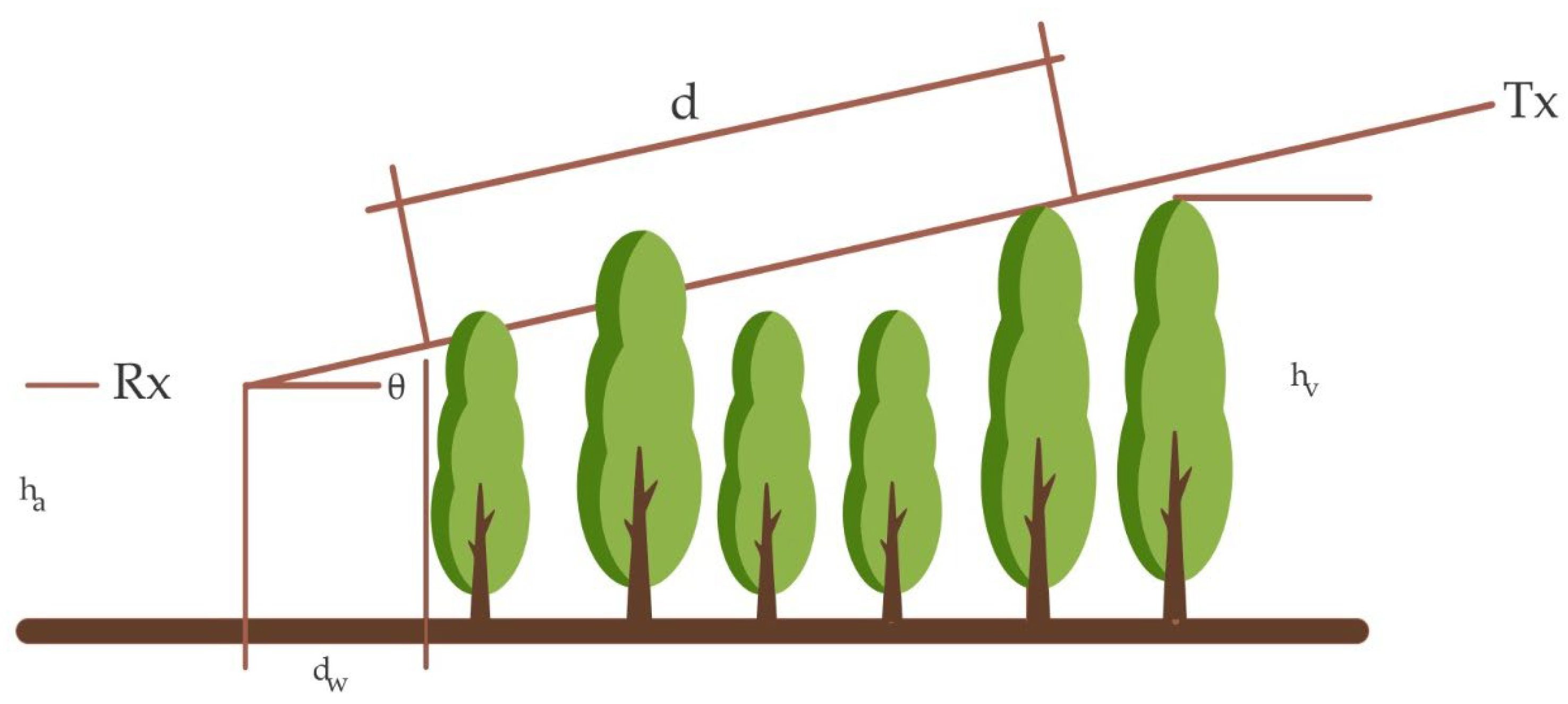
Sensors, Free Full-Text

Wireless vs Wired Video Transmission for Live Broadcast
How is radio signal propagated. 2 Comparison of wired and wireless transmissions WiredWireless BandwidthDepending on the media used, can be large Narrow. - ppt download

How is radio signal propagated. 2 Comparison of wired and wireless transmissions WiredWireless BandwidthDepending on the media used, can be large Narrow. - ppt download

How is radio signal propagated. 2 Comparison of wired and wireless transmissions WiredWireless BandwidthDepending on the media used, can be large Narrow. - ppt download

Radio Signal Interference > Wireless LAN Implications, Problems, and Solutions